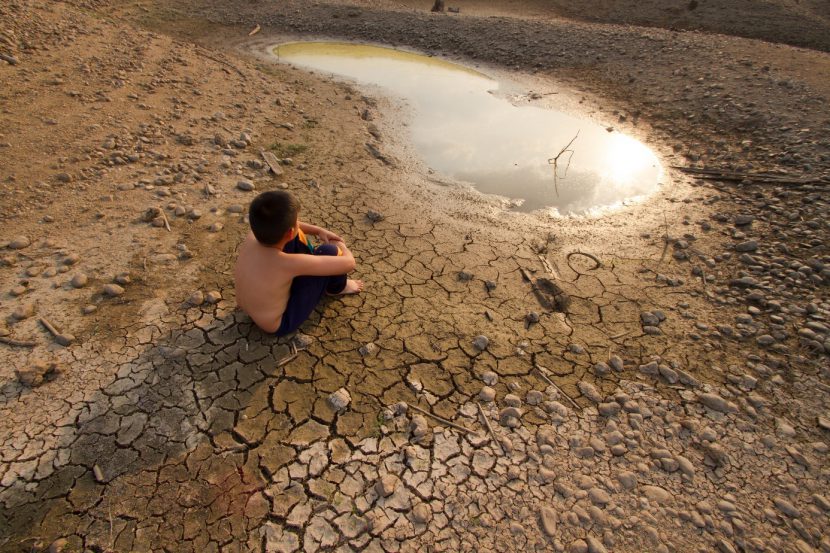
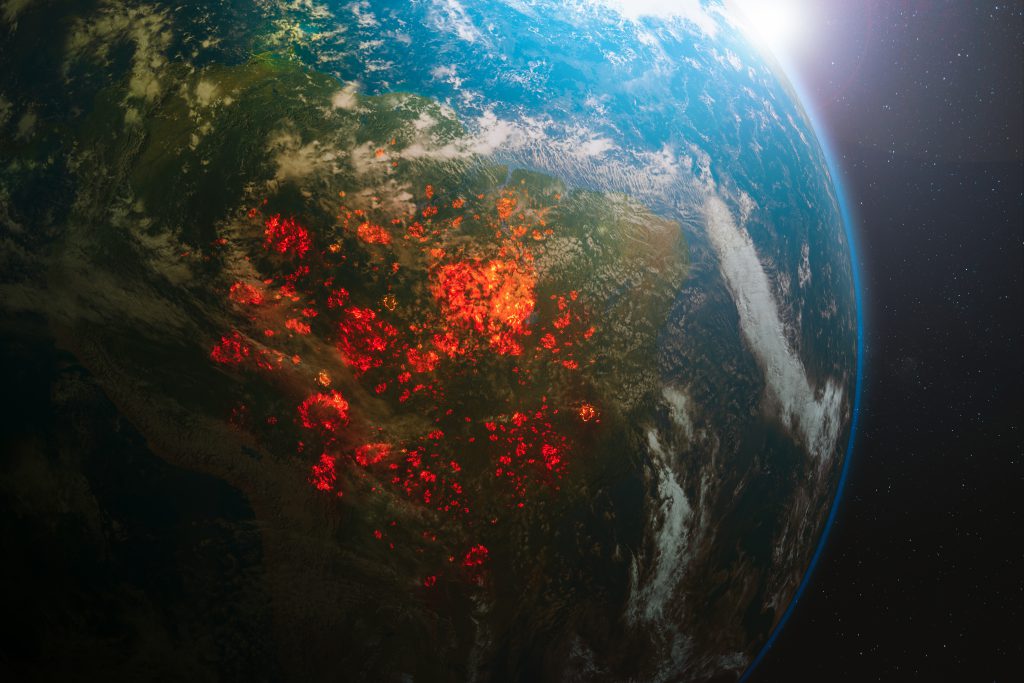
It has been 30 years since the Convention on the Rights of the Child was adopted by the General Assembly of the United Nations on 20 November 1989. One of the central themes at this year’s anniversary events is climate change and its drastic consequences for children’s rights.
Climate change as a central theme of the anniversary of the Convention on the Rights of the Child
The 30th anniversary of the Convention on the Rights of the Child is being celebrated by the United Nations in New York City and Geneva. On September 25, the United Nations General Assembly was having a commemoration at United Nations Headquarters in New York. According to the speech of Henrietta Fore, the UNICEF Executive Director, the focus was on the new challenges to children’s rights.
The first challenge she mentioned was climate change. In doing so, she demands the adults to listen, support and “follow the lead” of those children who are protesting against climate politics. (Henrietta Fore, 2019) Environmental and climate protection are also on the agenda for the upcoming commemorative event in Geneva which is scheduled for the end of November (Université de Geneve, 2019).
The Convention on the Rights of the Child at a glance

The Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC) is the first legally binding universal agreement that recognizes children, which are defined as persons under the age of 18, unless they are have already reached the age of majority under applicable law (Article 1 CRC), as independent individuals with non-negotiable rights.
The Member States of the Convention have committed to respect, protect and promote the rights of the child. In total, the Convention on the Rights of the Child includes 54 articles containing civil, political, economic, social and cultural rights for children. (OCHR, 30 Years CRC, 2019) Member States’ compliance with the Convention is controlled by the Committee on the Rights of the Child (Protocol II to the CRC).
Currently, the Convention on the Rights of the Child has 196 Member States. The only state in the world that has not yet joined the Convention are the United States. (OCHR, status of ratification)
Climate change threatens children’s rights
Although no explicit right to climate protection is enshrined in the Convention on the Rights of the Child, the implementation of climate-damaging measures or the omission of climate protection measures essentially violate children’s rights.
Already, the dramatic effects of climate change are reflected in significant changes in temperature, precipitation and sea level rise. The frequency and intensity of climate risks and hazards, such as floods, drought, extreme weather events, the spread of diseases, glacial and permafrost melts are steadily rising. This creates threats to the economy, global water supply, agricultural resources, ecosystems, health and forestry. (UNFCCC 2019, p.2)
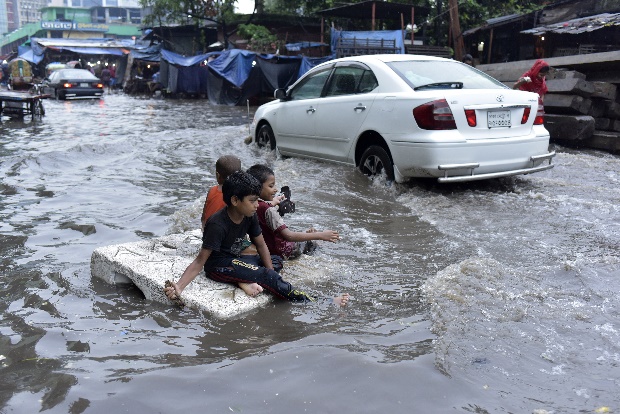

These effects of climate change put at risk the rights of the child (Article 3 CRC), life (Article 6 CRC) and health (Article 24 CRC) and decent living conditions (Article 27 CRC). Furthermore, climate change affects the long-term protection of ethnic minorities (Article 30 CRC). These are often particularly affected by climate change, such as the Inuit by melting the ice in the Arctic.
Indirectly, climate change can affect many other children’s rights, such as the right to education (Article 28 CRC) if schools are destroyed or their families can no longer afford to attend school because of the financial consequences of climate change. In connection with all these threats, the realization of children’s rights (Article 4 CRC) cannot be guaranteed. (Guillemot/Burgess)
As the Convention on the Rights of the Child obliges the Member States to protect children’s rights, they violate the Convention if they do not take, as far as they are able, adequate measures to counteract climate change.
Communication procedure: 16 children fight against child rights violations caused by climate policies
“Change needs to happen now if we are to avoid the worst consequences.” (Greta Thunberg, Press Conference on Communication Procedure, 2019)
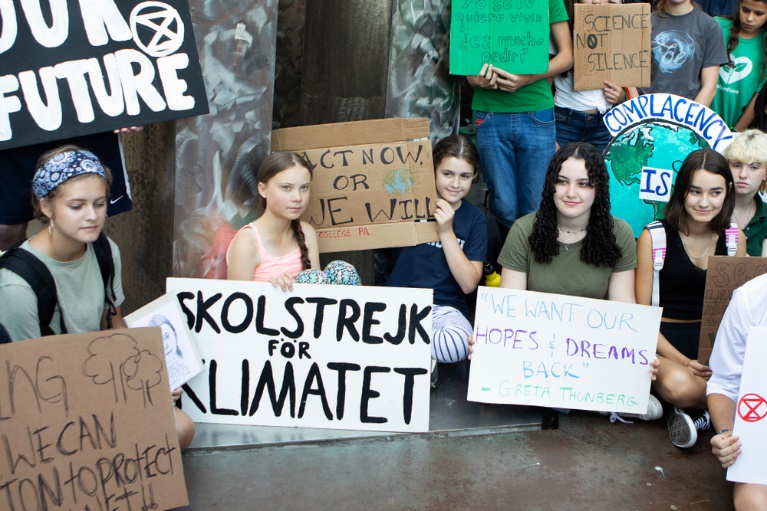
Sixteen children from twelve different states between 8 and 17 years have submitted a complaint about children’s rights violations by omitting climate policy measures to the Committee on the Rights of the Child. Among the complainants is the 16-year-old Swedish climate protection activist Greta Thunberg, who became known as the founder of the student movement “Fridays for Future”. (UNICEF, 2019)
The communication procedure is a legal instrument of the Convention on the Rights of the Child, which was launched five years ago by the Third Optional Protocol to the Convention. The complaint will allow children to take action at international level before the Committee on the Rights of the Child against the violation of their rights by States, if that State has ratified the Protocol. However, the decision taken by the Committee is not legally binding. (Optional Protocol 3 to the CRC)
The complaint is directed against the five states of Argentina, Brazil, France, Germany and Turkey, because they are, according to the complainants, large and influential G20 states which ignore climate change and therefore fail to protect children’s rights (UNICEF, Press Conference on the Child Rights Complaint, 2019). Currently, the Children’s Rights Committee is handling the children’s complaint. The result of the communication procedure remains to be seen. (Voytko, 2019)
We must counteract climate change
Climate change is more than an ecological problem. The effects of climate change not only affect the weather, they affect the habitats, living conditions and lives of all people, and especially children. It is high time we all join the activists, recognize the serious effects of climate change and oppose climate change.
At Humanium, we are committed to protecting the climate. Only if we can ensure the children sustainable and safe living conditions, we can also realize children’s rights and provide the children with a sustainable and secure future. And we are committed to ensure that those children’s rights, which were set out in the Convention on the Rights of the Child 30 years ago, not only have a symbolic character, but are being implemented today and in the future.
Written by Giulia Welge
References:
Guillemot, Joy/ Burgess, Jazmin (UNICEF): Child at Risk: The Case for Joint Action on Climate Change, retrieved from: https://www.unicef-irc.org/article/928-child-rights-at-risk-the-case-for-joint-action-with-climate-change.html , accessed on 18.10. 2019.
Henrietta Fore (UNICEF), Speech CRC30 Commemoration Event (25.09. 2019), retrieved from: https://www.unicef.org/press-releases/unicef-executive-director-henrietta-fore-crc-30-commemoration-event, accessed on 18 October 2019.
Office of Civilian Human Rights (OCHR), Celebrating 30 years of the Convention on the Rights of the Child (2019), retrieved from: https://www.ohchr.org/EN/HRBodies/CRC/Pages/CRC30.aspx, accessed on 18 October 2019.
Office of Civilian Human Rights (OCHR), Ratification Status of Human Rights Treaties, retrieved from: https://indicators.ohchr.org/, accessed on 18 October 2019.
UN General Assembly, Convention on the Rights of the Child, 20 November (1989), United Nations, Treaty Series, vol. 1577, p. 3, retrieved from: https://www.refworld.org/docid/3ae6b38f0.html, accessed on 18 October 2019.
UNICEF, 16 children, including Greta Thunberg, file landmark complaint to the United Nations Committee on the Rights of the Child (23 September 2019), retrieved from: https://www.unicef.org/press-releases/16-children-including-greta-thunberg-file-landmark-complaint-united-nations, accessed on 18 October 2019.
UNICEF, Pressekonferenz zur Klimabeschwerde, retrieved from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RGf-SBar_r4, zuletzt abgerufen am 18.10. 2019.
United Nations Climate Change Secretariat (UNFCCC Secreteriat), Climate action and support trends (2019), retrieved from: https://unfccc.int/sites/default/files/resource/Climate_Action_Support_Trends_2019.pdf, accessed on 18 October 2019.
Université de Genève (Centre Interfacultaire en Droits de l’enfant), Celebrating 30 Years of the Convention on the Rights of the Child, Programme (2019), retrieved from: https://www.unige.ch/cide/fr/conference-30-ans/home/programme/, accessed on 18 October 2019.
Voytko, Lisette: Greta Thunberg and 15 Young People Target These 5 Countries To Fight Climate Change (23.09.2019), Forbes Magazine, retrieved from: https://www.forbes.com/sites/lisettevoytko/2019/09/23/greta-thunberg-15-young-people-file-legal-complaint-to-fight-climate-change/, accessed on 18 October 2019.


